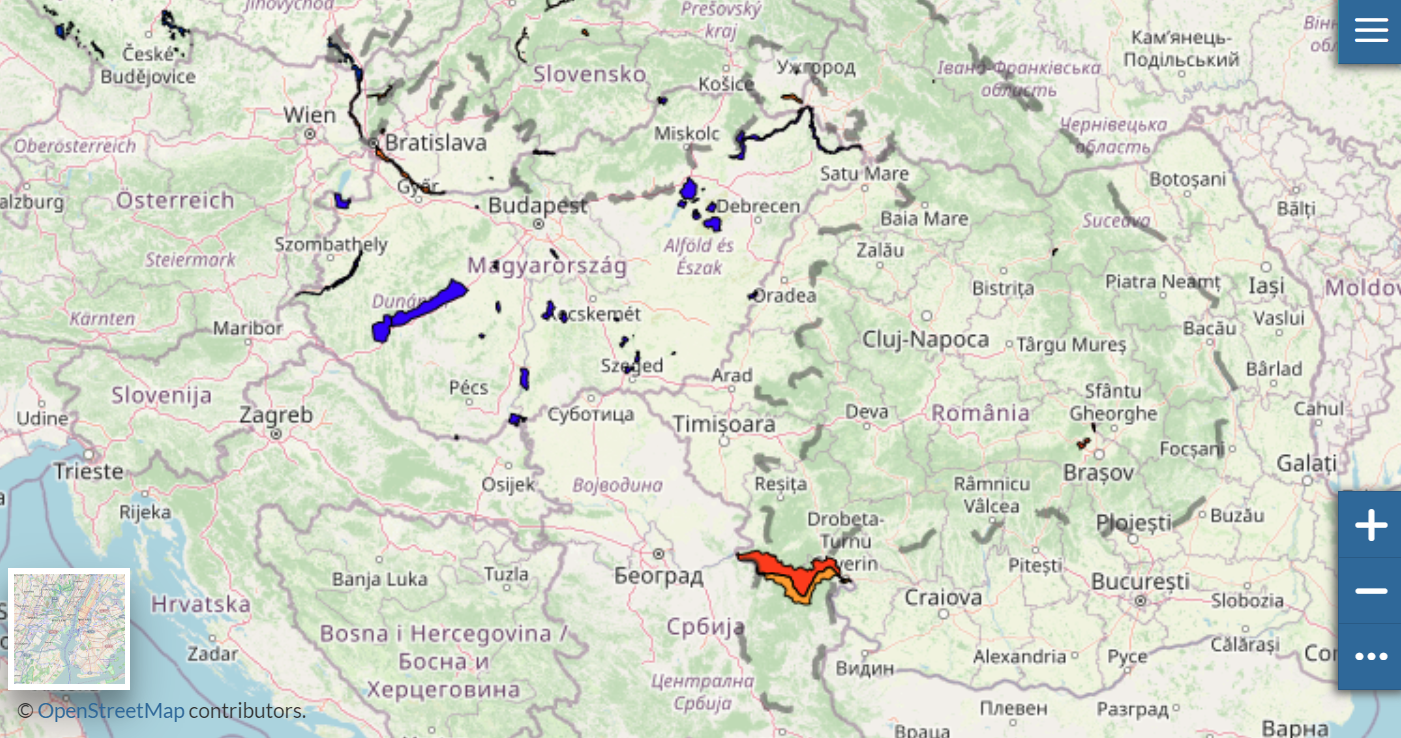
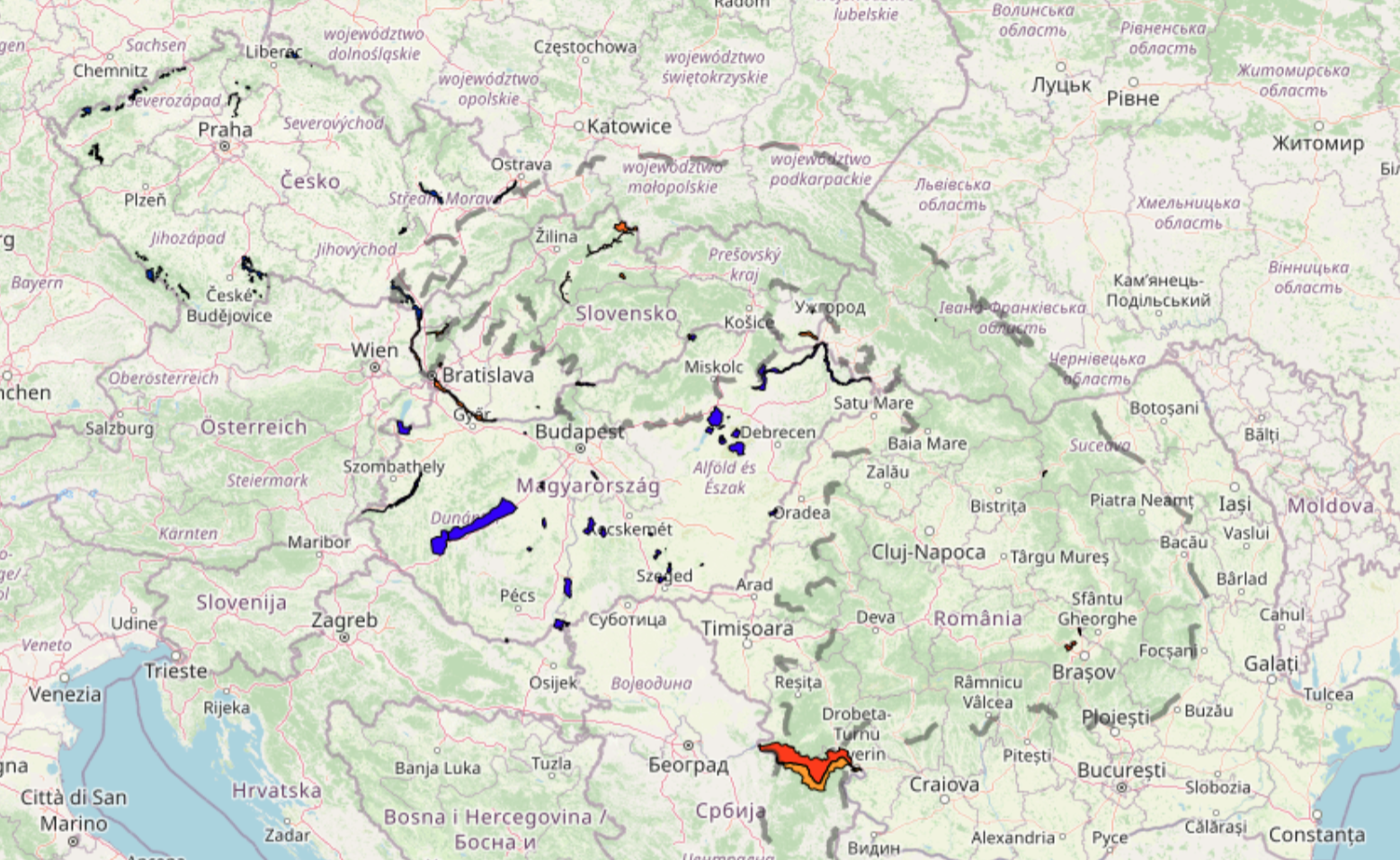
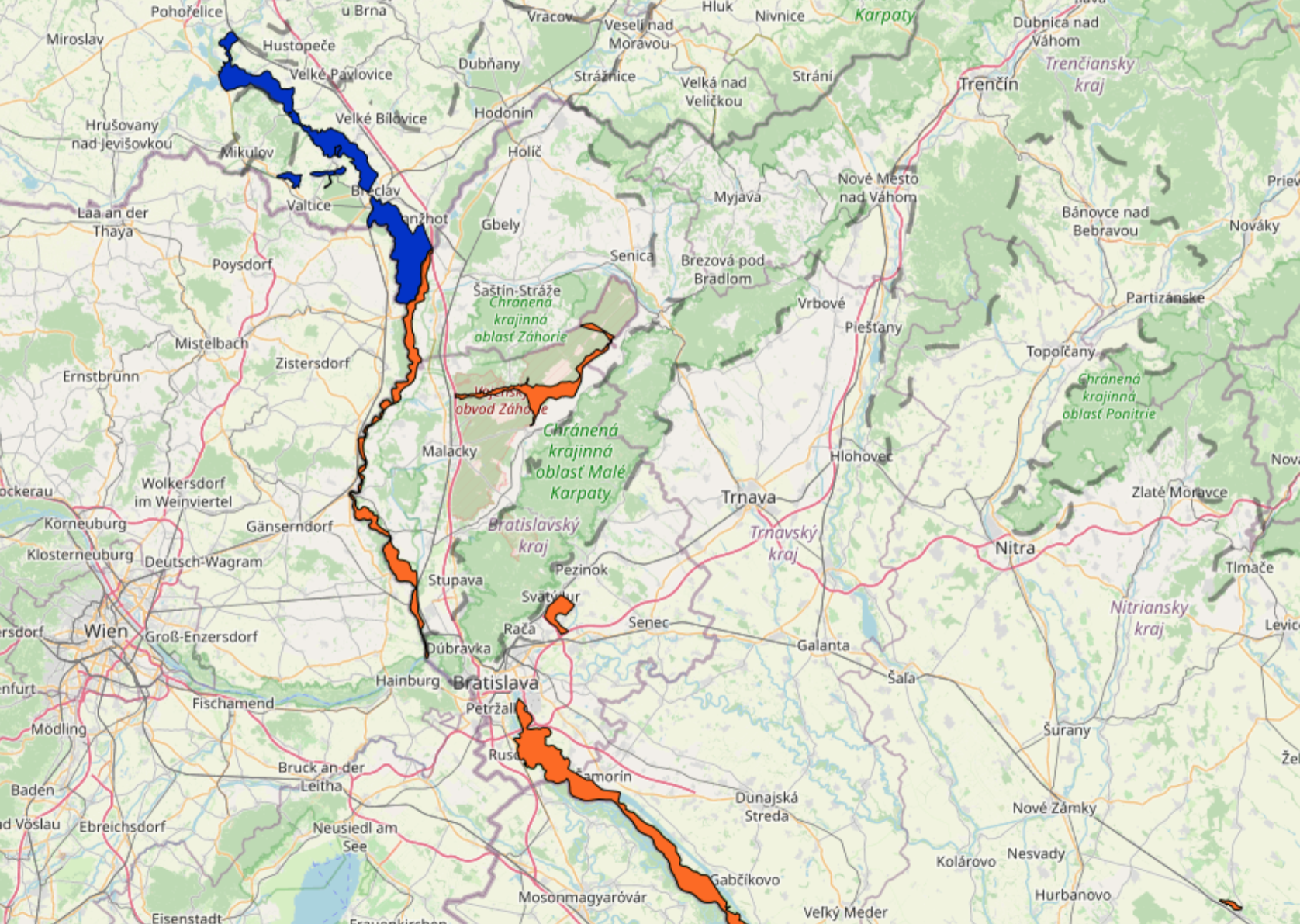
Thematic map Carpathian wetlands contains data about the wetlands in the Carpathian Ecoregion.
Wetlands are areas where water covers the soil, or is present either at or near the surface of the soil all year long or for varying periods of time during the year, including the growing season. Water saturation (hydrology) largely determines how the soil develops and the types of plant and animal communities living in and on the soil. Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species. The prolonged presence of water creates conditions that favor the growth of specially adapted plants (hydrophytes) and promote the development of characteristic wetland (hydric) soils.
The Convention on Wetlands is an intergovernmental treaty adopted on 2 February 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar and went into force in 1975. The official name of the treaty is „The Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat“, but it has become known as the Ramsar Convention. Nowadays the Convention has 168 (05/20124 Contracting Parties, or member States, in all parts of the world.
Originally the emphasis of the treaty was upon the conservation and the wise use of wetlands primarily as an habitat for water birds. During its existence, the Convention has extended its scope of implementation to cover all aspects of wetland conservation and wise use, recognizing wetlands as ecosystems that are extremely important for biodiversity conservation and for the well-being of human communities.
The most important part of the Convention is the creation of the List of Wetlands of International Importance ( the Ramsar List), with more than 2,180 wetlands. These wetlands cover more than 208 million hectares and have a status of special protection as Ramsar sites. The central Ramsar message is the need for the sustainable use of all wetlands.
For more information visit the website of Carpathian Wetland Initiative at https://www.cwi.sk/index.php